Welcome to my weekly cybersecurity roundup! Here, I share updates on the projects I’m currently working on, along with the most insightful cybersecurity videos I watched, articles I found valuable, and podcasts I tuned into this week.
Featured Analysis
Featured article analysis: The US Treasury’s OCC disclosed an undetected major email breach for over a year
This disclosure from the OCC should serve as a stark reminder of the persistent threats facing even well-resourced government agencies. The fact that a breach of this magnitude, compromising over 100 accounts and remaining undetected for over a year, highlights significant deficiencies in the OCC’s security posture and monitoring capabilities. The initial point of entry via a compromised administrator account underscores the critical importance of robust privileged access management, including multi-factor authentication and stringent auditing of administrative activities. Readers will note the delayed detection, reportedly triggered by an external notification from Microsoft, raising questions about the effectiveness of internal security controls and anomaly detection systems. The ongoing analysis to determine the full scope of the compromised data, including sensitive financial information, will be closely watched, as it could have broader implications beyond the OCC itself.
From a threat intelligence perspective, the unknown attribution of the attackers adds another layer of concern. While speculation about potential links to previous state-sponsored attacks targeting the Treasury exists, the lack of concrete evidence necessitates an investigation to understand the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed. The extended dwell time of the threat actors within the OCC’s email environment allowed for the exfiltration of a significant volume of emails, estimated at 150,000 since May 2023. This emphasizes the need for proactive threat hunting and advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions capable of identifying and neutralizing sophisticated intrusions before they can cause substantial damage.
Projects
- TryHackMe – Networking Secure Protocols – In Progress
Articles
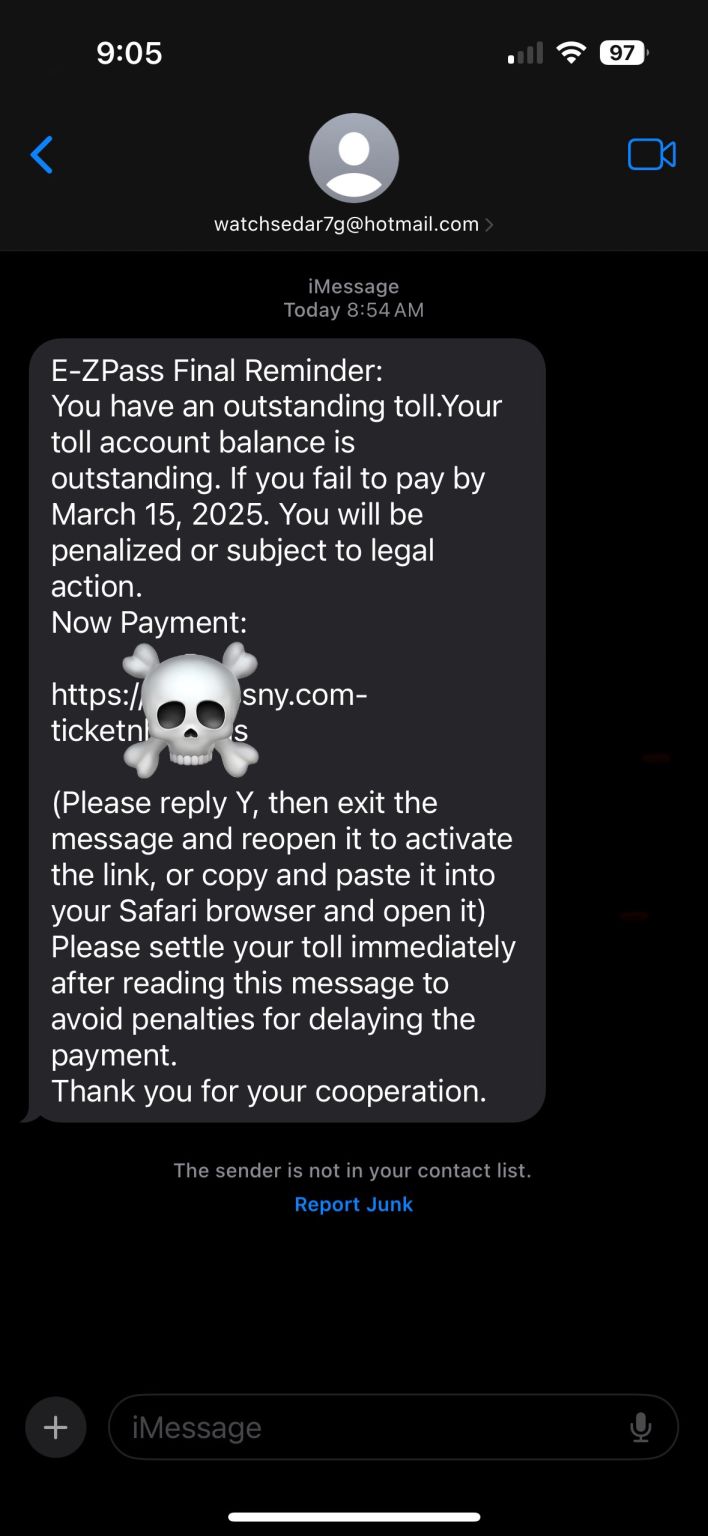
- Six arrested for AI-powered investment scams that stole $20 million – Spain’s police arrested six individuals behind a large-scale cryptocurrency investment scam that used AI tools to generate deepfake ads featuring popular public figures to lure people.
- New Mirai botnet behind surge in TVT DVR exploitation – A significant spike in exploitation attempts targeting TVT NVMS9000 DVRs has been detected, peaking on April 3, 2025, with over 2,500 unique IPs scanning for vulnerable devices.
- The US Treasury’s OCC disclosed an undetected major email breach for over a year – The US Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) disclosed a major email breach compromising 100 accounts, undetected for over a year.
- Nissan Leaf Hacked for Remote Spying, Physical Takeover – Researchers find vulnerabilities that can be exploited to remotely take control of a Nissan Leaf’s functions, including physical controls.
Podcasts
- Smashing Security 412: Signalgate sucks, and the quandary of quishing